CSCI 151 - Lab 11
Text Prediction
Overview
In this lab, we will implement a Trie for storing Strings and use it to
predict words as they are being typed.
Materials
Setup
- Download the skeleton for this project.
- Unpack the code into a new Eclipse Java project.
Description
Modern smartphones include keyboard assistants that will suggest words while
you are typing. There are many data structures that can be used to assist in this
interaction, to predict the remainder of words, and autocorrect typed words.
One such data structure is a Trie, which divides the words into their
component characters, and then stores the words in a minimal way
based on their overlapping characters. There are two main pieces to the model
of our code, a Trie to capture these characters in a tree-like structure,
and a SortedArray to store the list of children in sorted order.
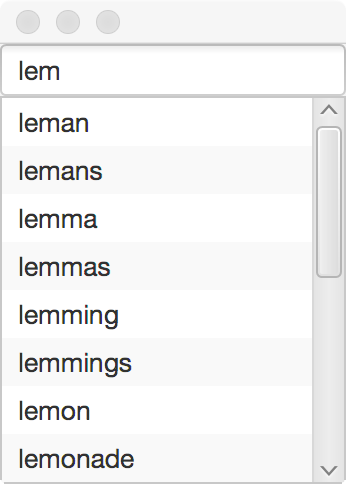
Methods that remain to be implemented in the SortedArray and Trie classes have been
marked with TODO for easy identification.
Step 1 - SortedArray
We wish to encapsulate an ArrayList, to add the functionality of being sorted,
while preventing a user from accidentally adding new nodes in an unsorted
fashion. Most of our methods will be mere wrappers for the corresponding
ArrayList methods, except the insert method, which should implement
an insertionSort algorithm.
Step 2 - size
To gain familiarity with the different components of the lab, first write a
method for a Trie that will return the number of words contained in a given Trie.
Step 3 - getChildWith
The getChildWith method should use the functionality of the
SortedArray to perform a linear search for a child Trie corresponding to the
given character. If a matching child Trie is not found, this
method should return null.
Step 4 - contains and add
Complete the contains and add methods of the Trie.
Contains ask the question: Is the given value a suffix of this Trie? Walk through the
tree, moving down to the appropriate child for each character
in value. If you fall off the tree, return false, otherwise
return true when the last child is contained in the Trie.
Add is implemented in a similar manner. Walk through the value, and add a new chain of
Trie nodes, one for each letter that is not already
found in the Trie. Mark the last Trie node as contained.
Step 5 - remove
Complete the method to remove a word from the Trie. This method should
walk down the tree, following the appropriate child, and save
the parent if there are other viable paths or if the parent
is the end of another word. Unmark the last node. Then
if it was an only child, remove the unneeded chain of
nodes from the last good parent.
Step 6 - Predicting the Text
Our algorithm for prediction is simple. As a user types in text, the Trie
will need to search for all words that can be made using what
the user is typing as a prefix. You will write two methods that can be
used in this way.
First, the inorder method will return an ArrayList of all
possible words to be created from a given Trie node. If the node is in the
middle of the Trie, it will only be returning suffixes.
Second, the successorsTo method will return an ArrayList
of all possible words to be created following a given prefix. The prefix
should be included in the words returned.
What to Hand In
Submit your SortedArray.java and Trie implementations.
Grading
- To earn a D, finish Steps 1 and 2.
- To earn a C, finish the above and Step 3 and 4.
- To earn a B, finish the above and Step 5.
- To earn a 100, finish the above and Step 6.
© Mark Goadrich, Hendrix College

